Pore Pressure Diffusion in Fractured Media (2020)
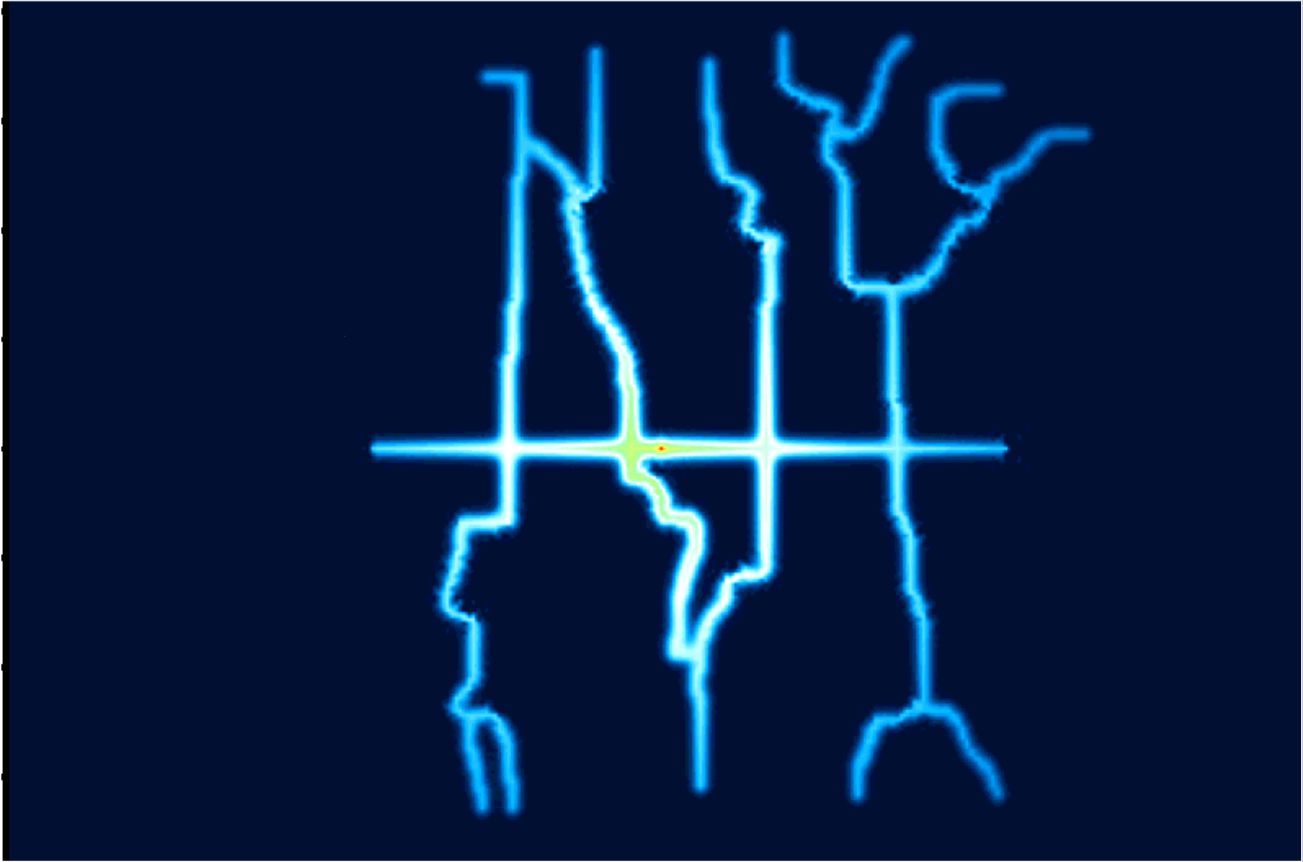
For fractured reservoirs with low permeability and low porosity, water injection is often needed during hydrocarbon production. Here, we proposed methods to accurately simulate pore pressure diffusion during water injection and to evaluate the diffusion flux from a complex fracture network.
We proposed to use explicit scalar coefficients of the anisotropic diffusion instead of a diffusion tensor at each lattice, and to assign these scalar coefficients in an elliptical form, with the major axis aligned with the fracture orientation. Based on these coefficients, we derived mathematical equations for calculating the flux of the pore pressure diffusion in fracture networks.
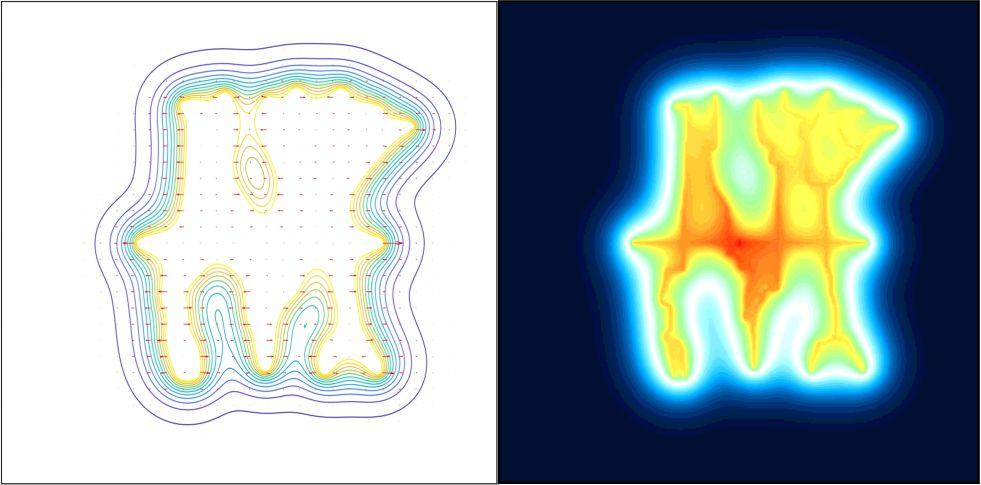
Numerical simulation of the anisotropic characteristic of diffusion with a prolonged water injection time revealed that although water injection affects pore pressure distribution mainly along the individual fractures during the early stage, it gradually affects the pore pressure of the media surrounding the fractures and changes the physical property of fractured media.
This article is published in GEOPHYSICS (2020, vol 85, no. 1), doi: 10.1190/geo2019-0169.1.